Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
Tags
- 전국대학생게임개발동아리연합회
- 위키북스
- 도커
- 인프라
- 온라인테스트
- 티스토리챌린지
- 스프링부트
- 백엔드
- Route53
- 생활코딩
- NAT gateway
- UNICON
- UNIDEV
- 자바개발자
- CICD
- 인디게임
- 게임개발동아리
- 프로그래밍
- 오블완
- 42서울
- 체크인미팅
- bastion host
- AWS
- 개발공부
- UNICON2023
- 라피신
- 백엔드개발자
- EC2
- 프리티어
- VPC
Archives
- Today
- Total
Hyun's Wonderwall
[데이터베이스] Chap 3. Introduction to SQL 본문
Outline
- SQL Data Definition
- Basic Query Structure of SQL Queries
- Additional Basic Operations
- Set Operations
- Null Values
- Aggregate Functions
- Nested Subqueries
- Modification of the Database
History
- IBM Sequel 언어: System R 프로젝트의 일환으로 IBM San Jose 연구소에서 개발됨
- 이후 이름을 변경 -> Structured Query Language (SQL)
- ANSI 및 ISO 표준
- SQL: SQL-86, SQL-89, SQL-92(일반적인 표준) SQL-1999, SQL-2003
- 상용 시스템은 SQL-92 기능을 대부분 또는 모두 제공하고, 이후 표준에서의 다양한 기능이나 특별한 자체 기능을 제공하기도 한다. (강의자료의 몇 예제가 MySQL 등 시스템에서 돌아가지 않을 수 있음)
SQL Parts (SQL의 구성)
SQL은 DDL과 DML의 기능을 모두 포함한다.
- DML(Data Manipulation Language): DB에서 정보를 조회, 튜플을 삽입, 삭제 및 수정. 데이터 조작과 관련.
DML의 예시: SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
- DDL(Data Definition Language): DB 구조를 정의 및 변경. 테이블 생성, 수정, 삭제와 같은 스키마 정의.
DDL의 예시: CREATE TABLE, ALTER TABLE, DROP TABLE, CREATE INDEX- DML - 데이터베이스에서 정보를 query하고 튜플을 삽입, 삭제, 수정할 수 있는 기능.
- Integrity - DDL이 integrity constraints를 specify하는 명령을 포함한다. (PK. FK.)
- View Definition - DDL이 뷰(가상의 테이블)를 정의하는 명령을 포함한다.
- Transaction control - 트랜잭션의 시작과 끝을 정의하는 명령을 포함한다.
- Embedded SQL과 dynamic SQL - general-purpose 프로그래밍 언어에 SQL문이 내장되는 방법을 정의한다.
- Authorization - relation 및 view에 대한 접근 권한을 지정하는 명령을 포함한다.
Data Definition Language
SQL의 DDL로 relation에 대한 정보를 명세.
- 각 relation의 schema (테이블 구조, 이름 등)
- 각 attribute의 값 type (속성 타입 정보)
- Integrity Constraints (무결성 제약 조건)
- 각 relation에 대해 유지관리될 indices(색인) 세트
- 각 relation에 대한 security 및 authorization 정보
- disk에 있는 각 relation의 physical storage structure (물리적 저장 구조)
Domain Types in SQL
- char(n): 고정 길이 n인 문자열
- varchar(n): 최대 길이 n인 가변 길이 문자열 // 동적 길이-> 메모리 더 효율적으로 사용 가능
- int: 정수형 (시스템 의존적인 정수의 유한 부분 집합)
- smallint: 작은 정수형 (시스템 의존적)
- numeric(p,d): p개 숫자로 이루어져 있는데 d개 숫자가 소수점 아래로 위치. 전체 p개, d가 소수점 밑에. 만약 더 큰 숫자 넣으면 짤림. 어떤 범위의 숫자를 다룰지 정확하게 알고 있는 경우 사용 가능.
- real, double precision: 실수.
- float(n): n개 digit을 표시할 수 있는 실수.
// DB마다 도메인 키워드 조금씩 다를 수 있음
Create Table Construct
create table 명령으로 SQL relation을 정의한다.
create table r // r: relation의 이름
(A1 D1, A2 D2, ..., An Dn, // Ai: relation r의 스키마에 있는 속성 이름
(integrity_constraint1), // Di: 속성 Ai의 도메인에 있는 값의 data type
...,
(integrity_constraint2))
Integrity Constraints in Create Table
- Integrity Constraints의 종류
- primary key (A1, ..., An) // PK
- foreign key (Am, ..., An) references r // FK
- not null // null 값 가지면 안됨
- SQL은 데이터베이스에 대해 무결성 제약조건을 어기는 업데이트를 막는다. 반드시 지키도록 DB가 체크함.
- ex.
create table instructor ( ID char(5), name varchar(20) not null, dept_name varchar(20), salary numeric(8,2), -- 소수점 포함해 전체 총 8자리, 소수점 이하 숫자가 2자리 primary key (ID), foreign key (dept_name) references department); - ID가 varchar이라는 것을 유의
create table student ( ID varchar(5), name varchar(20) not null, -- integrity constraints dept_name varchar(20), tot_cred numeric(3,0), primary key (ID), foreign key (dept_name) references department);create table takes ( ID varchar(5), course_id varchar(8), sec_id varchar(8), semester varchar(6), year numeric(4,0), grade varchar(2), primary key (ID, course_id, sec_id, semester, year), -- PK가 복합키 foreign key (ID) references student, foreign key (course_id, sec_id, semester, year) references section);create table course ( course_id varchar(8), title varchar(50), dept_name varchar(20), -- department를 참조함 credits numeric(2,0), primary key (course_id), foreign key (dept_name) references department);
Updates to tables
insert into r values (튜플)
: 소괄호 안에 한 개의 행 데이터를 작성하여 r에 튜플을 삽입.
delete from r
: r의 모든 튜플 삭제 (출력 시 아무것도 출력되지 x)
drop table r
: table r 자체를 삭제한다 (<-> create table ) 테이블 정의가 아예 삭제됨.
alter table r add A D
: r에 새 attribute를 추가한다. alter table test add explain varchar(20);
alter table r drop A
: r에서 A attribute를 삭제한다.
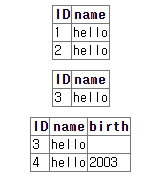
drop table test;
create table test (ID int, name varchar(10));
insert into test values (1, 'hello');
insert into test values (2, 'hello');
select * from test;
delete from test;
insert into test values (3, 'hello');
select * from test;
alter table test add birth numeric(4,0);
insert into test values (4, 'hello', 2003);
-- alter table test drop birth;
select * from test;
Basic Query Structure
- 기본적인 SQL 쿼리 형태:
select A1, A2, ..., An -- projection
from r1, r2, ..., rm -- cartesian product
where P -- selection, join - Ai: attribute / ri: relation / P: redicate
- SQL query의 결과물은 relation => 이 결과물로 또 다른 SQL을 할 수도 있다.
- SQL은 대소문자가 없다. (문자열에는 있다)
The select Clause
- select A from r
- SQL table은 중복된 행 허용. (관계대수는 튜플 중복 x. relation이 set이라.) (중복 column은 안 됨.)
- distinct: 중복 제거해 표시 / all: 그대로 모두 표시 (기본)
- *: 모든 attributes
- select _값_: 1개 열, 1개 행 갖는 테이블을 결과로 출력
- as: 컬럼 이름 rename
- arithmetic expression들을 사용한다: +, -, *, /
실험
select '437'; -- '437' 이름을 그대로 컬럼명으로 사용하고 값: 문자 437 (도메인: 문자형)
select 437; -- 437 이름을 그대로 컬럼명으로 사용하고 값: 437 (도메인: 숫자형)
select '437' as FOO 또는 'FOO'; -- FOO를 컬럼명으로 사용 (as 뒤에 숫자는 불가능)
select 'A' from instructor; -- A가 값인 'A' 컬럼 생기고 출력 (instructor의 tuple수만큼)
select *,'A' from instructor; -- instructor에 A가 값인 'A' 컬럼이 붙어 나옴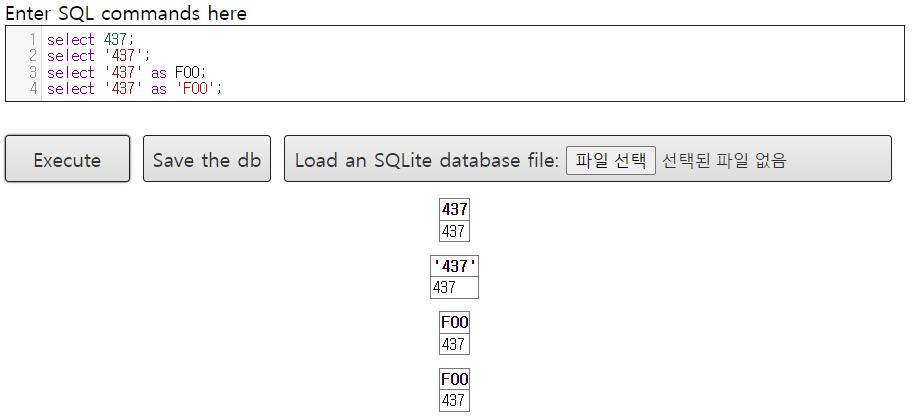
-- select ID, name, salary/12 from instructor;
select ID, name, salary/12 as monthly_salary from instructor;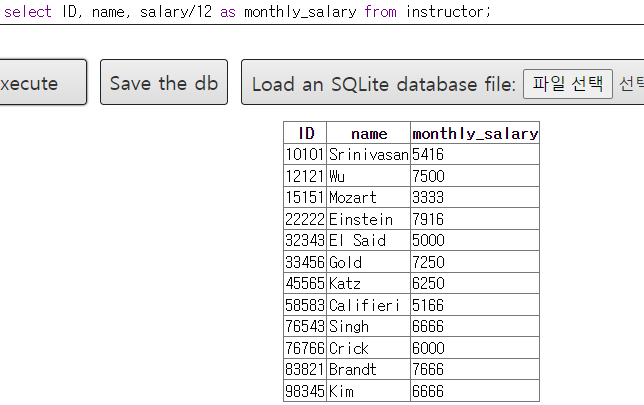
The where Clause
where clause는 result가 만족해야 하는 조건들을 명시한다. (selection에 대응)
- and, or, not logical connectives을 허용한다.
- 비교 연산자: <, <=, >, >=, =, <> // 이때 <>가 "다르다"이다.
select name from instructor where dept_name='Comp. Sci.'The from Clause
- from에서 ','로 연결하는것이 임이다.
- join = cartesian product + selection
Examples
- join 하기
- where에서 predicate들 and로 연결하기
The rename Operation
as clause로 relations과 attrubutes의 이름을 renaming할 수 있다.
키워드 as는 생략될 수 있다.
db에서 한 개의 테이블인 것을 query에서 두 개의 테이블인 것처럼 사용한다. 복제처럼.
select distinct T.name
from instructor as T, instructor as S
where T.salary>S.salary and S.dept_name='Comp. Sci.'
-- 컴퓨터공학과 교수의 최저연봉이 65000이므로 모든 학과 교수 중 연봉이 65000을 넘는 교수들의 이름이 출력된다
Self Join Example
relation emp-super
-- 'Bob'의 상급자 찾기
select supervisor from emp_super where person='Bob';
-- 'Bob'의 상급자의 상급자 찾기
select S.supervisor from emp_super-super S, emp_super T where S.person='Bob' and S.supervisor=T.person;String Operations
- like: where에서 문자열 비교를 위한 string-matching 연산자
- like는 %, _ 두 종류 문자를 사용하여 설명되는 패턴을 사용함.
- percent(%): 아무 문자열 (길이 0일 수 있음)
- underscore(_) : 아무 1개 문자
- 문자와 문자열 모두 따옴표를 꼭 붙여야 한다!!
- escape로 escape character로 사용할 문자를 지정.
like '100\%' escape '\' - ex. 부분 문자열 "dar"을 포함하는 모든 교수들의 이름을 찾기
select name from instructor where name like '%dar%' - 패턴들은 case sensitive!(대소문자를 구분.)
- 패턴 일치 예제들
- 'Intro%': "Intro"로 시작하는 아무 문자열
- '%Comp%': "Comp"를 하위 문자열로 포함하는 모든 문자열
- '___': 정확히 3자인 문자열
- '___%': 최소 3자 이상의 문자열
- SQL은 다양한 문자열 연산을 지원한다.
- concatenation (||) // 'A'||'B' == 'AB'
- 대소문자 변환
- 문자열 길이 구하기, substring 추출 등
Ordering the Display of Tuples
- order by attribute_name : tuple 결과를 해당 attribute를 기준으로 정렬
- 기본: 오름차순(asc) / 내림차순은 desc를 끝에 붙인다.
- order by 뒤에 여러 attributes를 나열하면 순서대로 고려해 정렬한다.
select distinct name from instructor order by name;select * from student order by name desc;select * from instructor order by dept_name, name; // 정렬 순서: (1)학과순 (2)이름순
'Subjects > 데이터베이스' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [데이터베이스] Chapter 5: Advanced SQL (0) | 2024.06.11 |
|---|---|
| [데이터베이스] 4. Intermediate SQL (0) | 2024.06.11 |
| [데이터베이스] 3. Introduction to SQL (2) (0) | 2024.06.11 |
| [데이터베이스] Chap 2. Intro to Relational Model (0) | 2024.04.15 |
| [데이터베이스] Chap 1. Introduction (0) | 2024.04.14 |




